Radon Facts
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) and the Surgeon General’s Office have estimated that as many as 20,000 lung cancer deaths are caused each year by radon. Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer. Radon-induced lung cancer costs the United States over $2 billion dollars per year in both direct and indirect health care costs. (Based on National Cancer Institute statistics of 14,400 annual radon lung cancer deaths – Oster, Colditz & Kelley, 1984)
According to the US EPA, nearly 1 in 3 homes checked in seven states and on three Indian lands had screening levels over 4 pCi/L, the EPA’s recommended action level for radon exposure.
The alpha radiation emitted by radon is the same alpha radiation emitted by other alpha generating radiation sources such as plutonium.
A family whose home has radon levels of 4 pCi/l is exposed to approximately 35 times as much radiation as the Nuclear Regulatory Commission would allow if that family was standing next to the fence of a radioactive waste site. (25 mrem limit, 800 mrem exposure)
An elementary school student that spends 8 hours per day and 180 days per year in a classroom with 4 pCi/l of radon will receive nearly 10 times as much radiation as the Nuclear Regulatory Commission allows at the edge of a nuclear power plant.(25 mrem limit, 200 mrem exposure)
Most U.S. EPA lifetime safety standards for carcinogens are established based on a 1 in 100,000 risk of death. Most scientists agree that the risk of death for radon at 4 pCi/l is approximately 1 in 100. At the 4 pCi/l EPA action guideline level, radon carries approximately 1000 times the risk of death as any other EPA carcinogen. It is important to note that the action level is not a safe level, as there are no “safe” levels of radon gas.
What is Radon?
Radon is a cancer-causing radioactive gas. You cannot see, smell or taste radon, but it may be a problem in your home. The Surgeon General has warned that radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States today. If you smoke and your home has high radon levels, you’re at high risk for developing lung cancer. Some scientific studies of radon exposure indicate that children may be more sensitive to radon. This may be due to their higher respiration rate and their rapidly dividing cells, which may be more vulnerable to radiation damage.
Radon can be found all over the U.S.
Radon comes from the natural (radioactive) breakdown of uranium in soil, rock and water and gets into the air you breathe. Radon can be found all over the U.S. It can get into any type of building —homes, offices, and schools — and result in a high indoor radon level. But you and your family are most likely to get your greatest exposure at home, where you spend most of your time.
You should test for radon.
Testing is the only way to know if you and your family are at risk from radon. EPA and the Surgeon General recommend testing all homes below the third floor for radon.
You can fix a radon problem.
Radon reduction systems work and they are not too costly. Some radon reduction systems can reduce radon levels in your home by up to 99%. Even very high levels can be reduced to acceptable levels.
How Does Radon Get Into Your Home?
Any home may have a radon problem
Radon is a radioactive gas. It comes from the natural decay of uranium that is found in nearly all soils. It typically moves up through the ground to the air above and into your home through cracks and other holes in the foundation. Your home traps radon inside, where it can build up. Any home may have a radon problem. This means new and old homes, well-sealed and drafty homes, and homes with or without basements.
Radon from soil gas is the main cause of radon problems. Sometimes radon enters the home through well water (see “Radon in Water” below). In a small number of homes, the building materials can give off radon, too. However, building materials rarely cause radon problems by themselves.
RADON GETS IN THROUGH:
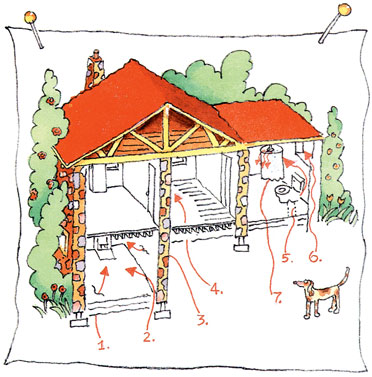 1. Cracks in solid floors
1. Cracks in solid floors
2. Construction joints
3. Cracks in walls
4. Gaps in suspended floors
5. Gaps around service pipes
6. Cavities inside walls
7. The water supply
Nearly 1 out of every 15 homes in the U.S. is estimated to have elevated radon levels. Elevated levels of radon gas have been found in homes in your state. Contact your state radon office for general information about radon in your area. While radon problems may be more common in some areas, any home may have a problem. The only way to know about your home is to test.
There are Two General Ways to Test for Radon
SHORT-TERM TESTING:
The quickest way to test is with short-term tests. Short-term tests remain in your home for two days to 90 days, depending on the device. “Charcoal canisters,” “alpha track,” “electret ion chamber,” “continuous monitors,” and “charcoal liquid scintillation” detectors are most commonly used for short-term testing. Because radon levels tend to vary from day to day and season to season, a short-term test is less likely than a long-term test to tell you your year-round average radon level. If you need results quickly, however, a short-term test followed by a second short-term test may be used to decide whether to fix your home.
LONG-TERM TESTING:
Long-term tests remain in your home for more than 90 days. “Alpha track” and “electret” detectors are commonly used for this type of testing. A long-term test will give you a reading that is more likely to tell you your home’s year-round average radon level than a short-term test.
What Your Test Results Mean
Test your home now and save your results. If you find high radon levels, fix your home before you decide to sell it.
The average indoor radon level is estimated to be about 1.3 pCi/L, and about 0.4 pCi/L of radon is normally found in the outside air. The U.S. Congress has set a long-term goal that indoor radon levels be no more than outdoor levels. While this goal is not yet technologically achievable in all cases, most homes today can be reduced to 2 pCi/L or below.
Sometimes short-term tests are less definitive about whether or not your home is above 4 pCi/L. This can happen when your results are close to 4 pCi/L. For example, if the average of your two short-term test results is 4.1 pCi/L, there is about a 50% chance that your year-round average is somewhat below 4 pCi/L. However, EPA believes that any radon exposure carries some risk – no level of radon is safe. Even radon levels below 4 pCi/L pose some risk, and you can reduce your risk of lung cancer by lowering your radon level.
If your living patterns change and you begin occupying a lower level of your home (such as a basement) you should retest your home on that level.
Even if your test result is below 4 pCi/L, you may want to test again sometime in the future.
Radon and Home Sales
More and more, home buyers and renters are asking about radon levels before they buy or rent a home. Because real estate sales happen quickly, there is often little time to deal with radon and other issues. The best thing to do is to test for radon NOW and save the results in case the buyer is interested in them. Fix a problem if it exists so it won’t complicate your home sale. If you are planning to move, read EPA’s pamphlet “Home Buyer’s and Seller’s Guide to Radon,” which addresses some common questions.
During home sales
- Buyers often ask if a home has been tested, and if elevated levels were reduced.
- Buyers frequently want tests made by someone who is not involved in the home sale. Your state radon office can assist you in identifying a qualified tester.
- Buyers might want to know the radon levels in areas of the home (like a basement they plan to finish) that the seller might not otherwise test.
Today many homes are built to prevent radon from coming in. Building codes in your state or local area may require these radon-resistant construction features. If you are buying or renting a new home, ask the owner or builder if it has radon-resistant features. The EPA recommends building new homes with radon-resistant features in high radon potential (Zone 1) areas. Even if built radon-resistant, every new home should be tested for radon after occupancy. If you have a test result of 4 pCi/L or more, consult a qualified mitigator to estimate the cost of upgrading to an active system by adding a vent fan to reduce the radon level. In an existing home, the cost to install a radon mitigation system is about the same as for other common home repairs.
Radon in Water
 There are two main sources for the radon in your home’s indoor air, the soil and the water supply. Compared to radon entering the home through water, radon entering your home through the soil is usually a much larger risk.
There are two main sources for the radon in your home’s indoor air, the soil and the water supply. Compared to radon entering the home through water, radon entering your home through the soil is usually a much larger risk.
The radon in your water supply poses an inhalation risk and an ingestion risk. Research has shown that your risk of lung cancer from breathing radon in air is much larger than your risk of stomach cancer from swallowing water with radon in it. Most of your risk from radon in water comes from radon released into the air when water is used for showering and other household purposes.
Radon in your home’s water is not usually a problem when its source is surface water. A radon in water problem is more likely when its source is ground water, e.g. a private well or a public water supply system that uses ground water. If you are concerned that radon may be entering your home through the water and your water comes from a public water supply, contact your water supplier.
If you’ve tested the air in your home and found a radon problem, and your water comes from a well, have your water tested.
If you’ve tested your private well and have a radon in water problem, it can be fixed. Your home’s water supply can be treated in two ways. Point-of-entry treatment can effectively remove radon from the water before it enters your home. Point-of-use treatment devices remove radon from your water at the tap, but only treat a small portion of the water you use and are not effective in reducing the risk from breathing radon released into the air from all water used in the home.
For more information, call EPA’s Drinking Water Hotline at (800) 426-4791 or visit www.epa.gov/safewater/radon.html If your water comes from a private well, you can also contact your state radon office.
How to Lower the Radon Levels in Your Home
Radon and Home Renovations
 If you are planning any major structural renovation, such as converting an unfinished basement area into living space, it is especially important to test the area for radon before you begin the renovation. If your test results indicate a radon problem, radon-resistant techniques can be inexpensively included as part of the renovation. Because major renovations can change the level of radon in any home, always test again after work is completed.
If you are planning any major structural renovation, such as converting an unfinished basement area into living space, it is especially important to test the area for radon before you begin the renovation. If your test results indicate a radon problem, radon-resistant techniques can be inexpensively included as part of the renovation. Because major renovations can change the level of radon in any home, always test again after work is completed.
Since there is no known safe level of radon, there can always be some risk. But the risk can be reduced by lowering the radon level in your home.
There are several proven methods to reduce radon in your home, but the one primarily used is a vent pipe system and fan, which pulls radon from beneath the house and vents it to the outside. This system, known as a soil suction radon reduction system, does not require major changes to your home. Sealing foundation cracks and other openings makes this kind of system more effective and cost-efficient. Similar systems can also be installed in houses with crawl spaces. Radon contractors can use other methods that may also work in your home. The right system depends on the design of your home and other factors.
Ways to reduce radon in your home are discussed in EPA’s “Consumer’s Guide to Radon Reduction.” You can also download a copy from our radon publications page.
The cost of reducing radon in your home depends on how your home was built and the extent of the radon problem. Most homes can be fixed for about the same cost as other common home repairs. The cost to fix can vary widely; consult with your state radon office or get one or more estimates from qualified mitigators. The cost is much less if a passive system was installed during construction.
Note: The diagram is a composite view of several mitigation options. The typical mitigation system usually has only one pipe penetration through the basement floor; the pipe may also be installed on the outside of the house.
Lowering high radon levels requires technical knowledge and special skills. You should use a contractor who is trained to fix radon problems. A qualified contractor can study the radon problem in your home and help you pick the right treatment method.
If you are considering fixing your home’s radon problem yourself, you should first contact your state radon office for guidance and assistance (see www.epa.gov/radon/whereyoulive.html) .
Most homes can be fixed for about the same cost as other common home repairs.
You should also test your home again after it is fixed to be sure that radon levels have been reduced. Most soil suction radon reduction systems include a monitor that will indicate whether the system is operating properly. In addition, it’s a good idea to retest your home every two years to be sure radon levels remain low.
The Risk of Living With Radon
 Scientists are more certain about radon risks than from most other cancer-causing substances.
Scientists are more certain about radon risks than from most other cancer-causing substances.
Radon gas decays into radioactive particles that can get trapped in your lungs when you breathe. As they break down further, these particles release small bursts of energy. This can damage lung tissue and lead to lung cancer over the course of your lifetime. Not everyone exposed to elevated levels of radon will develop lung cancer. And the amount of time between exposure and the onset of the disease may be many years.
Like other environmental pollutants, there is some uncertainty about the magnitude of radon health risks. However, we know more about radon risks than risks from most other cancer-causing substances. This is because estimates of radon risks are based on studies of cancer in humans (underground miners).
Smoking combined with radon is an especially serious health risk. Stop smoking and lower your radon level to reduce your lung cancer risk.
Children have been reported to have greater risk than adults of certain types of cancer from radiation, but there are currently no conclusive data on whether children are at greater risk than adults from radon.
Your chances of getting lung cancer from radon depend mostly on:
- How much radon is in your home
- The amount of time you spend in your home
- Whether you are a smoker or have ever smoked
Radon Risk If You Smoke
| Radon Level | If 1,000 people who smoked were exposed to this level over a lifetime*… |
The risk of cancer from radon exposure compares to**… |
WHAT TO DO: Stop smoking and… |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 pCi/L | About 260 people could get lung cancer | 250 times the risk of drowning | Fix your home |
| 10 pCi/L | About 150 people could get lung cancer | 200 times the risk of dying in a home fire | Fix your home |
| 8 pCi/L | About 120 people could get lung cancer | 30 times the risk of dying in a fall | Fix your home |
| 4 pCi/L | About 62 people could get lung cancer | 5 times the risk of dying in a car crash | Fix your home |
| 2 pCi/L | About 32 people could get lung cancer | 6 times the risk of dying from poison | Consider fixing between 2 and 4 pCi/L |
| 1.3 pCi/L | About 20 people could get lung cancer | (Average indoor radon level) | (Reducing radon levels below 2 pCi/L is difficult.) |
| 0.4 pCi/L | About 3 people could get lung cancer | (Average outdoor radon level) | Note: If you are a former smoker, your risk may be lower. |
| Note: If you are a former smoker, your risk may be lower. * Lifetime risk of lung cancer deaths from EPA Assessment of Risks from Radon in Homes (EPA 402-R-03-003). ** Comparison data calculated using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s 1999-2001 National Center for Injury Prevention and Control Reports. |
|||
Radon Risk If You’ve Never Smoked
| Radon Level | If 1,000 people who never smoked were exposed to this level over a lifetime*… | The risk of cancer from radon exposure compares to**… | WHAT TO DO: |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 pCi/L | About 36 people could get lung cancer | 35 times the risk of drowning | Fix your home |
| 10 pCi/L | About 18 people could get lung cancer | D20 times the risk of dying in a home fire | Fix your home |
| 10 pCi/L About | 18 people could get lung cancer | 20 times the risk of dying in a home fire | Fix your home |
| 8 pCi/L | About 15 people could get lung cancer | 4 times the risk of dying in a fall | Fix your home |
| 4 pCi/L About | 7 people could get lung cancer | The risk of dying in a car crash | Fix your home |
| 2 pCi/L About | 4 person could get lung cancer | The risk of dying from poison | Consider fixing between 2 and 4 pCi/L |
| 1.3 pCi/L( | About 2 people could get lung cancer | (Average indoor radon level) | Reducing radon levels below 2 pCi/L is difficult.) |
| 0.4 pCi/L ( | (Average outdoor radon level) | Reducing radon levels below 2 pCi/L is difficult.) | |
| Note: If you are a former smoker, your risk may be higher. | |||
Radon Myths
MYTH: Scientists aren’t sure radon really is a problem.
FACT: Although some scientists dispute the precise number of deaths due to radon, all the major health organizations (like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the American Lung Association and the American Medical Association) agree with estimates that radon causes thousands of preventable lung cancer deaths every year. This is especially true among smokers, since the risk to smokers is much greater than to non-smokers.
MYTH: Radon testing is difficult, time consuming and expensive.
FACT: Radon testing is easy. You can test your home yourself or hire a qualified radon test company. Either approach takes only a small amount of time and effort.
MYTH: Homes with radon problems can’t be fixed.
FACT: There are simple solutions to radon problems in homes. Hundreds of thousands of homeowners have already fixed radon problems in their homes. Most homes can be fixed for about the same cost as other common home repairs; check with one or more qualified mitigators. Call your state radon office for help in identifying qualified mitigation contractors.
MYTH: Radon affects only certain kinds of homes.
FACT: House construction can affect radon levels. However, radon can be a problem in homes of all types: old homes, new homes, drafty homes, insulated homes, homes with basements, homes without basements. Local geology, construction materials, and how the home was built are among the factors that can affect radon levels in homes.
MYTH: Radon is only a problem in certain parts of the country.
FACT: High radon levels have been found in every state. Radon problems do vary from area to area, but the only way to know your radon level is to test.
MYTH: A neighbor’s test result is a good indication of whether your home has a problem.
FACT: It’s not. Radon levels can vary greatly from home to home. The only way to know if your home has a radon problem is to test it.
MYTH: Everyone should test their water for radon.
FACT: Although radon gets into some homes through water, it is important to first test the air in the home for radon. If your water comes from a public water supply that uses ground water, call your water supplier. If high radon levels are found and the home has a private well, call the Safe Drinking Water Hotline at 1 800-426-4791 for information on testing your water.
MYTH: It’s difficult to sell homes where radon problems have been discovered.
FACT: Where radon problems have been fixed, home sales have not been blocked or frustrated. The added protection is some times a good selling point.
MYTH: I’ve lived in my home for so long, it doesn’t make sense to take action now.
FACT: You will reduce your risk of lung cancer when you reduce radon levels, even if you’ve lived with a radon problem for a long time.
MYTH: Short-term tests can’t be used for making a decision about whether to fix your home.
FACT: A short-term test, followed by a second short-term test* can be used to decide whether to fix your home. However, the closer the average of your two short-term tests is to 4 pCi/L, the less certain you can be about whether your year-round average is above or below that level. Keep in mind that radon levels below 4 pCi/L still pose some risk. Radon levels can be reduced in most homes to 2 pCi/L or below.
